Treatment of Yeast Infections in Men and Women
This post features an overview of differences between treatment options for yeast infection in males and females.
What is yeast infection?
Yeasts are fungi (plural of fungus) that are normally found in our bodies and live in peace. They are also found in our environment. Most of them are harmless and cause infections when the defense system of our body is weak, giving them an opportunity to thrive. There are many yeasts that can infect us, Candida being the most common.
Causes
As we know that yeasts are the cause of opportunistic infections (when given the opportunity), they grow best in certain conditions and are kept under check in other. Some of the causes of yeast infections are:
- Too much intake of carbohydrates like sweet potatoes, dairy products etc.
- Antibiotic treatments
- Warm and humid weather with non-ventilating clothing. These conditions increase fungal growth
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Weak immune system (including HIV)
- Stress
Symptoms
Yeasts can have symptoms on many parts of the body including the genitalia (sex organs), food pipe (esophagus), mouth, etc. Some of them are:
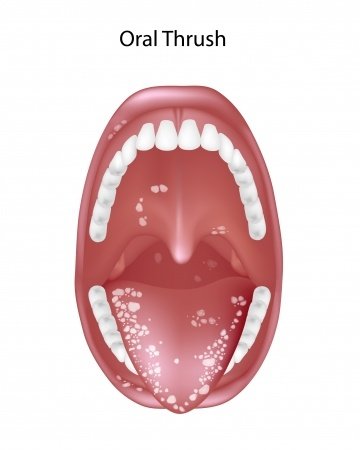
- Oral thrush – whitish covering on tongue and/or inside mouth
- Esophagitis – infection of food pipe with difficulty in swallowing
- Vaginitis – infection of vagina with burning sensation, vaginal discharge and itching
- Difficulty in urination – burning sensation
- Itching near the rectum
- Decreased libido (sex drive) and difficult sexual life (pain during coitus)
Incidence of yeast infections in Males vs. Females
Yeast infections are commonly thought of as the infections of females alone. This is not the case. Research has shown that males are equally prone to this infection. General population is not aware of this fact because males tend not to report it to their physicians that they are suffering from it. Most of the time they think of it not as a threat. It is important to state here that yeast infections are not gender-specific.
- Among Women: Women are more commonly infected by yeast infections. In fact it is the second most common type of vaginal infection (bacterial infection is at the top of the list). More than 70% of the women get at least one fungal infection in their lifetime. Vaginal irritation and white smelly discharge are the common manifestations of candida infection (a yeast) in women.
- Among Men: An important question here is, “Can men get yeast infection?” The answer is, yes! Men can get yeast infection if they adopt an unhygienic lifestyle. Most of the time they contract this infection from their partner during unprotected sexual activity who is suffering from yeast infection. Red rash and itching on the penis are the common manifestations, including those already mentioned above. Diabetic and immune suppressed males have more chances of getting this infection as well as uncircumcised males.
Yeast infections, though not gender-specific, are much more common in females than males. This prevalence should be kept in mind while going through the rest of the document that follows.
Diseases and Treatment
Once fungal infection is confirmed, the plan of action then is to use antifungal drugs. Many of these drugs are available with different ranges of activity against different fungi (yeasts). The treatment plan against each individual yeast infection is discussed below:
- Vaginal Candidiasis (infection with Candida): Irritation of the vagina and foul smelling discharge are the major complaints in women. It is treated with over the counter antifungal drugs in the form of creams like Monistat or Clotrimazole. Oral antifungals may be required for resistant infections. Use of yogurt is helpful. Yogurt contain a bacteria, which helps keep the environment of vagina acidic. The acidic environment restricts fungal growth, therefore yogurt has proved beneficial. In the same token, men need to guard their genitalia. Unprotected sex can cause infection in men who carry this infection from their partner.
- Oral Thrush: The incidence of oral thrush is same in both males and females, more common in children. It is treated by local application of Clotrimazole. Amphotericin B is used in most severe cases. Nystatin “swish and swallow” is also used. Mouthwash and lemon juice also have some effect in controlling fungal overgrowth.
- Esophageal Candidiasis: The difficulty and pain in swallowing needs attention in this condition. The drug of choice for esophageal candidiasis is Fluconazole. Caspofungin or micafungin can also be used as an alternative treatment.
- Cryptococcus Meningitis: (infection with Cryptococcus neoformans). Amphotericin B and Flucytosine are used in combination for meningitis (with symptoms of headache, fever and stiff neck). In patients of HIV, fluconazole is also used.
- Aspergillosis: (infection with Aspergillus). It is an infection of nose and respiratory tract with symptoms like pain in sinuses, swelling of face and sometimes pneumonia (condition of the lungs with difficulty in breathing, chills, fever and cough). It is treated with either amphotericin B given by intravenous injection or voriconazole given orally.
- Histoplasmosis: (infection with Histoplasma capsulatum). The infection by this fungus produces symptoms of fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath and weight loss. Amphotericin B is the treatment of choice. Fluconazole or itraconazole are given for long term therapy.
- Coccidioidomycosis: (infection with Coccidioides immitis). This infection is commonly known as Valley Fever. Breathing in (inhaling) the fungal particles (spores) is the way of getting infected with this disease. The symptoms include fever, headache, cough, fatigue and stiffness of joints. This can be treated by intravenous injections of amphotericin B. Sometimes the treatment in mild cases is initiated with oral fluconazole.
Prevention
It goes beyond saying that prevention is better than cure. Fungal infections can sometimes be embarrassing for a person as it mostly involves the private parts of the body. The best way to go about it is to take all the precautionary measures available and avoid getting the infection in the first place. Some of the precautionary measures are:
- Adopt a hygienic lifestyle – females should keep their genitalia clean and wash it after urination. Males should also keep their genitalia clean.
- Eat healthy – avoid consuming too much carbohydrates.
- Take a bath daily – this allows staying clean.
- Dress properly – women should keep the region of folds between legs dry as moist and warm areas of skin harbor yeast.
- Avoid stress – this builds up immune system.
- Avoid taking too many antibiotics.
- Avoid unprotected sex - especially for men.
- Exercise regularly – this boosts immunity.
- Sleep tight.
Conclusion
Fungal infections are not so common but one should not take anything for granted. Health is a blessing and one should do his/her best to remain so. Yeast infections are more common in women with treatments differing with respect to different diseases in men and women. Fungal infections can sometimes be very serious if not take care of, especially in immune compromised individuals (HIV+ or those after an organ transplant). The advancement in medicine these days provides cure for most of the diseases and one can totally get rid of it, but it is important to take all the precautions available at hand. Avoiding the disease is always better than getting infected and then relying on medication. Keeping a strong immune system is always handy in this regard.
| Written by: | Michal Vilímovský (EN) |
|---|---|
| Education: | Physician |
| Published: | January 27, 2014 at 3:55 AM |
| Next scheduled update: | January 27, 2016 at 3:55 AM |
Related articles
Get more articles like this in your inbox
Sign up for our daily mail and get the best evidence based health, nutrition and beauty articles on the web.


Ache in left arm that you should not ignore
Alkaline water dangers: why you should not drink it
How to Avoid Sleepiness While Studying?
23 Foods That Increase Leptin Sensitivity
Low dopamine (e.g. dopamine deficiency): causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options
Swollen taste buds: the ultimate guide to causes, symptoms and treatment
Thin endometrial lining: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Pimples inside nose: the complete guide
Holes in tonsils: definition, symptoms, treatment and prevention
How to deal with an ingrown hair cyst
Allegra vs. Zyrtec vs. Claritin
How to get rid of phlegm (excessive mucus) in throat? Detailed guide to medical and home remedies, symptoms and causes
What causes stomach ache after meals?
Allergy to penicillin and alternative antibiotics
Liver blood test results explained