Beetroot: Overview of health benefits and risks
Beetroot is also known as the table beet, golden beat, garden beet, red beet or simply as the beet. Beetroot was first cultivated by the Romans. They are of great commercial value since the 19th century, when it was discovered that it could be converted to sugar. They are most commonly cultivated in North America, Central America, Europe, USA, Russia, France, Poland and Germany. They belong to family ‘Beta vulgaris’.
There are many varieties of beet, which are available throughout the year. Typically it of deep purple color, but can also be white or golden. Both the leaves and root of beet can be eaten. The leaves have a bitter taste whereas the root is sweet. Beet has a delicious, distinctive flavor and a high nutritional status.
For thousands of years beetroot has been associated with sexuality and has been used as an aphrodisiac. It is frequently used as an ingredient for soups, pickles and salads and is also used as a natural coloring agent. It has been gaining popularity as a new super food based upon the result of the latest researches that beets and beetroot juice can increase blood flow, improve athletic performance and lower blood pressure.
Nutritional highlights of beetroot
Beetroot is of great nutritional value. It is rich in calcium, iron, minerals and vitamins A and C. It is an excellent source of folic acid, fiber and organic compounds like carotenoids, lutein/zeaxanthin, glycine, betaine. Betaines function to reduce the concentration of homocysteine, a chemical that has been associated with the risk of heart diiseases. It also contains a variety of vitamins and minerals like thiamine, riboflavin, vitamin B6, pantothenic acid, choline, betaine, magnesium, phosphorus, manganese, potassium, zinc, copper and selenium. Beet is also a good source of anthocyanins-beneficial flavonoids.
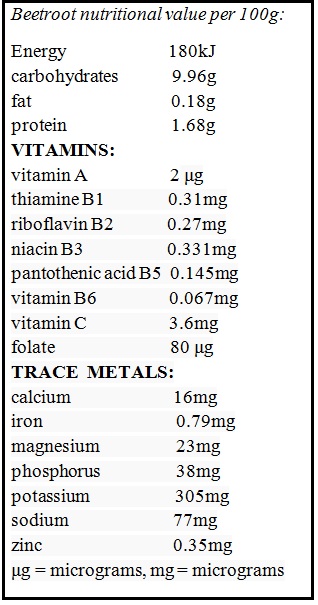
It is loaded with nitrate too. Nitrate is responsible for increase in athletic performances, but on the other side, it causes health risks too. Beetroot fiber has antioxidant properties due to the presence of enzymes like glutathione peroxidase. It has been shown to increase the number of white blood cells, which detect and fight against harmful bacteria and virus. Beets are rich in glutamine, an amino acid, beneficial for the health and maintenance of the gastrointestinal tract.
Beetroot contains a very low quantity of fat, with no cholesterol, but they possess the highest sugar content of all vegetables. Beets should not be overcooked as they lose 25% of their folate when cooked.
Foods
Beetroot can be eaten either grilled, boiled, or steam roasted. Beets can also be eaten raw or canned. Raw beetroot is usually served in salads. Additionally, raw beets can also be juiced. Beet can be cooked as a vegetable. Commercially beetroot is processed into pickles or canned food. Pickled beets serve as a traditional food in South America. The green colored leaves are also edible. They are usually bitter in taste but you can boil them to decrease the degree of bitterness. As beets are bright red in color they are excellent for garnishing and presentation of meals.
- Fresh beetroot: Fresh beetroot can be eaten raw. All you need is to peel it off. Fresh beetroot can be added to a salad or sandwich. Health benefits of fresh beetroot are great.
- Canned beetroot: When beets are fully grown and fully nutritious they can be picked and canned. Canned beets are low in calories as compared to the fresh beetroot. 1 cup of sliced canned beets contains 12 grams of carbohydrates, 1.6 grams of protein and 0.2 grams of fat. They function as an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and heart’s friend substances.
- Beetroot juice: It is known as a super food. It provides a number of benefits like it lowers blood pressure, prevents peripheral artery diseases, boosts athletic performance, prevents heart, liver and eye problems, and relief skin problems.
Health benefits of beetroot
Beets have a wide range of health benefits because of their high nutritional content. In this article we will discuss all the plus points about beetroot one by one.
Beets as an aphrodisiac
One of the first known uses of beet from the ancient times is as an aphrodisiac. It was first used by the Romans for this purpose. It improves sexual health and stamina. It is also known as ‘natural Viagra’ because it works by the same mechanism as that medicine. Since beet is a rich source of nitrates, it boosts your sexual health. It helps release nitric oxide into your body. Nitric oxide widens the blood vessels, and increases the blood flow to the sex organs.
Beets contain large amount of boron, a chemical compound which is directly linked to the production of the human sex hormone. This leads to an increase in your libido, increased fertility, enhanced sperm mobility, and a reduction in your frigidity. In short, you can improve your sexual life a lot by adding beets to your daily diet.
Beets as antihypertensive
Beetroot can help reduce blood pressure. This is because the fact that beetroot is rich in nitrates and produces nitric oxide in the blood. Nitric oxide causes widening of blood vessels and lowering of blood pressure. A research was conducted to find out the relationship between beetroot and its effect on blood pressure. It was found that consumption of about 500 grams of beetroot or 500ml of beetroot juice every day reduces a person’s blood pressure in about six hours.
Beets contain potassium as well. Potassium is a vasodilator- it dilates the blood vessels. When vessels are dilated they become relaxed. This lowers the blood pressure throughout the body.
Beets are your heart’s friend
A body deficient in potassium has a high risk of heart attack. Therefore beetroot, a potassium rich vegetable, is recommended for your heart’s health. Potassium is called a vasodilator. When blood vessels are dilated and blood pressure is reduced, clots are less likely to form. Beets also lower the chances of accumulation of already formed plaque.
So, beets beat clots that can eventually lead to heart attacks and stroke. Beets, by gradually lowering blood pressure over the period of 24 hours, decreases risk. Beets convert dietary nitrate (NO3) to nitrite (NO2) and then to nitric oxide. Nitric oxide regulates the blood flow. It retards clogging of blood vessels by inhibiting platelet aggregation and recruitment of inflammatory cells. Nitric oxide can also be generated by the oxidation of L-arginine by endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nitrite provides protection against ischemia/reperfusion injury in the myocardial vasculature indicating that it plays an important role in cardiovascular homeostasis.
A daily dose of 1 to 2 cooked beetroot or 500ml of beetroot juice can help significantly reduce blood pressure and its associated risks.
Beets as antioxidants
Beets contain betacyanin, the pigment that gives color to beetroot. Betacyanin is an antioxidant. Antioxidants are substances that protect healthy cells from damage by free radicals. Vitamin C is another important antioxidant present in beet. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant. It boosts your immunity and defends your body against free radicals. It promotes the activity of white blood cells, which are the main defenders of the body. That way it provides resistance to the body against a number of viral, bacterial and fungal infections.
Beets beat osteoporosis
Beet is packed with mineral ‘silicon’. Silicon is an important constituent of the body. It helps the body to utilize calcium efficiently. Calcium is a very important mineral necessary for the healthy bones, teeth and muscles. 1 glass of beetroot juice a day reduces the risk of osteoporosis (a progressive bone disease that causes bones to lose mass and become weak).
Beets are great for pregnant females
Since beets are a rich source of folic acid they are good for pregnant females and their fetuses. Folic acid is a necessary nutrient for the proper development of the baby’s spinal cord during first 3 months of pregnancy. Folic acid deficiency could lead to spina bifida (a congenital disorder of the spinal cord, in which spinal cord does not develop properly).
Beetroot also provides extra energy needed to boost the pregnant females, which is required during pregnancy. Another amazing quality of the beetroot is that it has an abundant supply of iron. Iron is necessary for the mother as well as the fetus. Iron is needed for the production of red blood cells as well as protects the body from fatigue. Pregnant females must remember that cooked beetroot has 25% lower levels of folic acid than raw beetroot.
Beets prevent plaque formation and atherosclerosis
Beets are good for health as they prevent plaque formation and decrease the level of LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol). Beets contain a large amount of soluble fibers. Beet fiber has cholesterol lowering capabilities. It reduces triglycerides as well. It increases the level of good cholesterol- HDL cholesterol. HDL is a defense line against many heart and liver problems. The fiber also works to strip away excess LDL cholesterol. There are carotenoids and flavonoids in beets that can help prevent LDL from being oxidized and deposited onto the artery walls. Beetroot is also known to contain a compound ‘betacyanin’. Betacyanin gives purplish-red color to beetroot. It is a powerful antioxidant. It helps prevent the oxidation of LDL cholesterol. It resists the deposition of LDL on the wall of the arteries as well as it assists the body to eliminate LDL quickly. This protects the heart from risk of potential heart attacks, stroke and atherosclerosis. Another important component of beet is betaine. This nutrient lowers the levels of homocysteine in the body, which can be potentially harmful to the blood vessels and heart.
Beet as a cure for anemia
Iron is vital for the body. Although both sexes are dependent on iron for blood cells formation, females require a bit more, especially during pregnancy, lactation and menstruation. It is a common myth that all red colored food items are rich in iron. There is a partial truth hidden in the myth. Beets contain a lot of iron. Iron plays a leading role in the production of red blood cells. Iron combines with a protein haem to form hemoglobin. This hemoglobin combines with the oxygen to form a compound called oxy-hemoglobin. Oxy-hemoglobin is a part of the blood, which helps transport oxygen and nutrients to various parts of the body. Deficiency of iron leads to anemia known as iron deficiency anemia. Vitamin C, another component of beet, also assists in treating anemia as it increases iron absorption in the body. Remember anemia can occur due to other causes too.
Beets are good for diabetics
Beetroot contains sugar, but it is virtually fat free and low in calories. It has a medium glycemic index (GI) of 64. Medium GI means that it releases blood sugars slowly. This property stabilizes a person’s blood sugar level while satiating the sugar craving. Beetroot has an extremely low Glycemic Load of 2.9, meaning that it is converted into sugars very slowly. This, therefore, helps the body to keep blood sugar levels stable. So, there is good news for all diabetics that you can fulfill your sweet craving with a little beetroot.
Beets boost brain function and prevent dementia
Beetroot increases the uptake of oxygen by the body. A study showed that drinking beetroot juice could increase a person’s stamina and brain function by 16%. This is attributed to its high nitrate content. Nitrate is responsible for proper functioning of the brain. It helps in the transmission of nerve impulses. This makes the brain work better and beats dementia. Betaine present in beets is helpful in treatment of depression. Beet is also blessed with tryptophan, an amino acid, which relaxes the mind and creates a sense of well-being.
Beets treat constipation
Beets keep your stomach healthy and ward off constipation. It has high content of soluble fiber. Beetroot adds bulk to your diet and works as a laxative. It cleanses the stomach and intestines. It regulates your bowel habits. Beet and its juice are valuable for nutritionists. They use it to detect stomach acid levels.
Beets protect you from cancer
Studies have shown that beets are good at preventing skin, lung, and colon cancer. They contain the pigment betacyanin, which antagonizes cancerous cell growth. A study conducted at the Howard University has shown that betacyanin slows the growth of breast and prostate tumors by 12.5%. Flavonoid in beets has some tumor inhibiting effect. Vitamin C also reduces the chances of cancer.
One of the anti-cancer effects of beetroot relates to its high iron content. Iron helps in the regeneration of red blood cells that delivers more oxygen to the cancer cells. The higher the oxygen, higher will be the cellular respiration. Cellular respiration helps to kill cancer cells and eliminate waste products. Preservatives used in meats, especially nitrates can prompt the production of nitrosamine compounds in the body which can cause cancer. Studies have proved that beet juice prevents the cell mutations caused by these compounds. Beet juice also slows down tumor development. Another important component of beet juice that exhibit anti-cancer activity is betanin. Add some beets to the weekly diet to keep your body cancer-free!
Beets improve sports performance
A lot of researches were conducted to find out the relationship between beets and athletic performance. It was found that beets can significantly improve athletic performance and can help you run fast. The component of beet that is responsible for these effects is nitrate.
People who drink beet juice have an increased rate of oxygen uptake due to its high nitrate content. Nitrates increase oxygen uptake by 16%, much more than that can be achieved by extensive training. It increases person’s stamina for participation and performance in sports. This makes the beet juice a super sports drink. The results of various studies suggest that nitrate supplementation by beet juice has the potential to improve athletic performance in events lasting five to 30 minutes.
Beets are a rich source of energy and relieves fatigue
Beetroot contains a significant amount of carbohydrates that are essential for health and are fuels for energy. Beetroot is loaded with a number of vitamins and minerals. It boosts a person’s energy. This is due to high nitrate and iron content. Nitrates dilate vessels and iron helps in oxygen transportation. Both components increase oxygen delivery to cells, thereby increasing a person’s stamina and energy. So, beets help prevent fatigue.
Beets are liver friendly
Beets have been shown to help cleanse, strengthen the liver and stimulate the functions of the liver. It works as a tonic for the liver, purifier for the blood, and can prevent various forms of liver cancer. Beta cyanin in beetroot can help your liver in the detoxification process. It helps the body to eliminate harmful toxins. It also prevents the build-up of fatty deposits in the body.
Beet as an immunity booster
Beetroot has an amazing range of nutrients and vitamins that can really boost your immune system. It helps your body to fight better against microorganisms. It also acts as an antioxidant. It ensures re-oxygenation of damaged cells and stimulates the production of new blood cells. This property of beetroot is very helpful for your body.
Beets can cheer you up
Nature has included betaine in beetroots, which enhances the production of serotonin. Serotonin is a body’s natural mood lifter. So, fresh beetroot can literally make you smile and can cheer you up!
Beets are healthy for your skin
Beet juice is healthy for your skin as it promotes the growth of healthy skin and hairs. It is also beneficial in the prevention and treatment of acne and helps to eliminate blemishes.
Health risks of beetroot
When taken in moderate quantity beetroot is safe for most people. Beet is also safe when used as a medicine. Excess of everything is bad; same is true for beetroot too. Some of the side effects of excessive beetroot consumption are as follows:
Kidney problems
Beets can cause lowering of body calcium levels. Intake of too much beets might damage kidney and might make kidney disease worse. If you have kidney stones you should avoid foods containing oxalates. As beetroot also contains oxalates it can hinder the absorption of calcium in the body. Whenever absorption of calcium is hindered, chances of kidney stone formation are increased.
Pigmentation
According to the British Dietetic Association, beetroot contains some flavonoids known as anthocyanins. Anthocyanins are responsible for the formation of deep pigments on the body.
Beeturia
An interesting side effect of beetroot is that it can turn urine pinkish red in about 10 to 15% of people. This reddening of the urine is known as beeturia. It can be confused with blood, but this is not literally blood. This phenomenon is not harmful in itself, but it can be an indicator of an underlying problem. Mostly it is associated with problem with iron metabolism. People with iron excess or iron deficiency are much more likely to experience beeturia than normal healthy individuals. So, if you experience beeturia you have to suspect iron associated problems and should consult a doctor.
Iron and copper conditions
People with iron and copper diseases, like hemochromatosis and Wilson disease, should avoid excessive consumption of beetroot. Hemochromatosis is a disorder that occurs because of excess iron in the body. Wilson disease is a form of copper overload in the body.
Pregnancy
Pregnant women should take betaine containing foods with care. As beetroot is packed with betaine it is rated “C” for use during pregnancy. C rating indicates that beet is safe for use in pregnant and lactating women in regular amount but, it is a mystery that whether it will be safe in larger amount or not. Beetroot have shown an adverse effect on pregnant animal.
Interactions of beetroot
Beetroot has a significant amount of betaine. Betaine has mild side effects like nausea, diarrhea and stomach upset. People with kidney disease should avoid betaine. Betaine can increase body cholesterol levels, especially when taken in conjunction with folic acid, vitamin B6 or vitamin B12. Obese or overweight people should also avoid betaine as it can increase cholesterol.
| Written by: | Michal Vilímovský (EN) |
|---|---|
| Education: | Physician |
| Published: | June 10, 2014 at 2:40 AM |
| Next scheduled update: | June 10, 2016 at 2:40 AM |
Get more articles like this in your inbox
Sign up for our daily mail and get the best evidence based health, nutrition and beauty articles on the web.


Ache in left arm that you should not ignore
Alkaline water dangers: why you should not drink it
How to Avoid Sleepiness While Studying?
23 Foods That Increase Leptin Sensitivity
Low dopamine (e.g. dopamine deficiency): causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options
Swollen taste buds: the ultimate guide to causes, symptoms and treatment
Thin endometrial lining: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Pimples inside nose: the complete guide
Holes in tonsils: definition, symptoms, treatment and prevention
How to deal with an ingrown hair cyst
Allegra vs. Zyrtec vs. Claritin
Allergy to penicillin and alternative antibiotics
How to get rid of phlegm (excessive mucus) in throat? Detailed guide to medical and home remedies, symptoms and causes
What causes stomach ache after meals?
Liver blood test results explained