Rheumatoid arthritis: causes, symptoms, treatment and complications
What comes to mind when you think of arthritis? You might think of sore joints and painful knees. But Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is something more than just the pain and swelling of joints. It is basically an auto-immune disorder that affects a number of body tissues including joints, skin, cardiovascular system, eyes, brain, liver and bones. Rheumatoid arthritis causes serious damage to body tissues causing their dysfunctioning and severe disabilities.
Human body has got an excellent defense system called immune system that protects our body from foreign invaders like viruses, bacteria and fungus. But sometimes this system backfires and the result is several autoimmune diseases, rheumatoid arthritis is one of such diseases.
Before we can move on to know more about this disease, it would be better here if you know the pathophysiology of this disease. And to understand the pathophysiology, you need to know some basics. Human immune system contains different type of cells. These cells include antigen presenting cells, B cells and T cells. Antigen presenting cells present foreign antigens (bacteria and viruses) to T cells and B cells. This is followed by an immune response in body mediated by antibodies (produced by B cells) and active killing of foreign invaders (mediated by T cells). Under normal conditions, these immune responses are kept under balance. But in RA these immune responses act in an exaggerated manner. Moreover, there is over production of several mediators of inflammation including Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-17. The combined effect of all these things is tissue damage and inflammation.
According to some estimates, rheumatoid arthritis effects 13.7 million adults in America alone and women are two to three times more prone to get this condition as compared to males. In the text to follow you’ll read everything you need to know about rheumatoid arthritis; including its causes, symptoms, treatment options and complications.
What are the causes of rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder of unknown etiology i.e. the exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is still unknown. There is no evidence that any physical injury or psychological trauma, like stress, triggers it. However, some researchers speculate that following might be some of the most important triggers for rheumatoid arthritis:
Genetic pre-disposition
Most researchers believe that rheumatoid arthritis is a genetic disorder i.e. it runs in families. Major histo-compatibility complex (MHC) is a component of body immune system that presents foreign antigens (bacteria, viruses) to the immune cells of our body (including B and T lymphocytes). The genes encoding for the production of MHC are called Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes. There are different types of HLA genes, encoding for different types of MHCs. Some of these HLA genes are DR0401 and DR0404. It is believed that people inheriting these genes are more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis.
One more gene group playing its role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis includes PTPN22 and PAD14. People that have these genes are more likely to develop this condition.
In nut shell, family history of rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most important causes for RA. If someone among your blood relations has got this condition, you’re more prone to develop this disorder.
Environmental factors
The relation between environmental factors and RA is still poorly understood. However, it is believed that smoking is perhaps one of the most important environmental factors contributing to the development of RA. This conclusion is based on the fact that the prevalence of RA in smokers is two to three times higher as compared to non smoker.
Researchers also speculate some relation between RA and alcohol consumption.
Vitamin D deficiency is also sometimes linked to be as one of the causes of RA. But this area still needs rigorous testing to know the validity of this fact.
Infections
It is believed that RA might develop as an exaggerated immune response of body to several infections including infections caused by Epstein bar virus (EBV) and Human herpes virus 6 (HPV-6).
What are the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
Although the most significant effect of Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is on the joints of human body but several other organs are prone to the damaging effect of this disorder. These structures include human eyes, brain, liver, bones, skin, lungs and kidneys. So, the symptoms vary depending on the organ affected. All these organs and associated symptoms are discussed in detail as follows:
Symptoms when joints are affected
If RA attacks different joints of body, following symptoms might be observed:
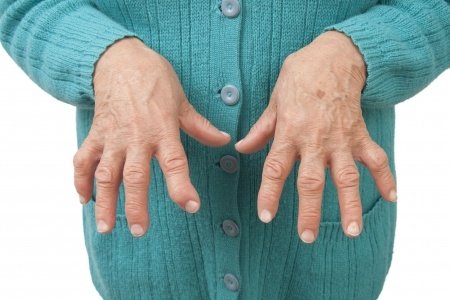
- The affected joints are swollen and warm.
- They’re painful to touch (tender).
- Movement of affected joints is usually very limited and painful.
- At first, only one or two joints might get affected. But with the passage of time, the number of affected joints increases (polyarthritis).
- The most commonly affected joints include small joints of spine, hands and feet. But in advanced stages, large joints including shoulder and knee joints might also show the symptoms of arthritis.
- Pain and swelling of joints is at its peak early in the morning. This is perhaps the most important sign that distinguishes rheumatoid arthritis from non-inflammatory arthritis.
- The joint damage may manifest itself in the form of pain and swelling but with the progression of disease associated structures like joint capsule, ligaments and tendons might also get damaged.
Symptoms when skin is affected
If the basic damage includes the damage of skin, following symptoms may appear:
- If the disease affects your skin, the most important symptom is the appearance of rheumatoid nodules (rounded elevated structures). These nodules are few millimeters to few centimeters in diameter. These nodules mostly appear on bony prominences of body including olecranon, metacarpophalangeal joint and calcaneal tuberosity.
- Some rare skin reactions include atrophy of fingers, redness of palms (palmar erythema), rice paper skin, peeling skin, sweet’s syndrome (appearance of red spots on skin associated with systemic symptoms like fever).
Symptoms when lungs are affected
The infection of lungs manifest as:
- The most important effect is fibrosis of lungs.
- Pleural effusion may develop (collection of gas or liquid in pleura surrounding the lungs).
- In advanced stages rheumatoid lung disease may develop. In this condition the structure of lungs is obliterated, lungs shrink and functionality of lungs is lost.
Symptoms when kidneys are affected
Rheumatoid arthritis causes following effects on Kidneys:
- It may cause inflammation of kidneys that might progress to renal amyloidosis (collection of abnormal proteins in kidneys).
- It may also damage glomerulus causing glomerulo-nephritis.
Symptoms when cardiovascular system is affected
The damaged caused to cardiovascular system manifests as:
- Atherosclerosis is the most important effect on cardiovascular system. Atherosclerosis may progress to heart attacks and strokes.
- Pericarditis (that manifests as chest pain), endocarditis and valvular degeneration might also be some manifestation of cardiovascular RA.
Symptoms upon the damage of other organs
A variety of other symptoms may appear:
- The infection of eyes may cause blurring or even loss of vision.
- You might experience of dryness of eyes and mouth (Sjorgen’s syndrome).
- Burning, itching and discharge from eyes are also common.
- You might experience difficulty in sleeping.
- Damage of liver can lead to hepatitis.
- Hameatological (blood) disease can lead to anemia and paleness of skin.
- Damage to nerves can cause tingling, burning and numbness of hand and feet- as occurs in carpel tunnel syndrome.
- Damage of bones can progress to osteoporosis.
- In addition, you might also experience generalized symptoms like loss of appetite, weight loss, generalized feeling of being ill (malaise), fatigue, intense pain in body parts during the morning and fever.
What are the possible complications of rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis can lead to severe complications like:
- Damage to lungs can progress to rheumatoid lungs (loss of functionality and shrinkage of lungs).
- Hardening and narrowing of blood vessels (atherosclerosis). It can further lead to a number of complications including elevated blood pressure, angina, heart attack, stroke and pericarditis.
- Osteoporosis of bones can lead to severe damage of spinal cord and other bones.
- The blood vessels can sometimes become inflamed (vasculitis).
- Liver damage can progress to hepatitis.
- Ocular damage can cause permanent blindness.
- Kidney damage can cause disturbed homeostasis.
- Damage to joints leave a person practically handicapped.
What are the treatment options?
There is no specific cure for RA. The only treatment is symptomatic treatment. This treatment strategy includes amelioration of the symptoms of the disease. These treatment options include:
Use of DMARDs
Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is the drugs of first choice when it comes to the cure of RA. These drugs not only lessen the systemic symptoms of RA but can actually reverse the tissue damage caused by this disease. A number of drugs are included in this group. These drugs include:
- Most important DMARD is methotrexate. Folate is one of the most important metabolite required for the normal division of immune cells, including T and B cells. Methotrexate actively blocks the production of folate thus deprives T and B cells from the basic thing they need. This suppresses the production of T and B cells- the most important reason for the development of this disease in first place.
- As explained earlier, over production of several mediators of inflammation is one of the most important reasons for excessive damage and swelling of tissues. Another strategy to limit RA attacks is to limit the production of these chemical mediators. One of these mediators include Tumor necrotic factor (TNF). Drugs like infliximab limit the production of TNF.
- Similarly, blockade of interleukin synthesis is an important mechanism for limiting the attacks of RA. Several drugs like Anakinra and Rituximab fall into this category.
Use of NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are another option for the symptomatic treatment of RA. Almost all the symptoms of RA are caused due to excessive inflammation. And different mediators (also including prostaglandins) are responsible for this inflammation. These mediators are produced through a chemical reaction catalyzed by an enzyme called COX (cyclo-oxygenase) enzyme. NSAIDs block the production of these mediators by two ways:
- Non selective COX inhibitors block both type 1 and type 2 COX enzymes. This group includes drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen.
- Selective COX inhibitors block type 2 COX enzymes. This group includes drugs like celecoxib.
Surgery
If joints are too severely affected to be cured by any conventional method, the last choice in that case is surgical correction of damaged joints. In this method, the affected joint parts are removed and are replaced by prosthetic structures. However, this process may require subsequent physiotherapy for proper recovery.
Alternative methods
Even use of drugs and surgery is no promising cure for this disease. Use of medicines may provide you some relief but the side effects are substantial. In fact, you might have to face more side effects than the benefits. You can try taking as much care of yourself as possible, as they say prevention is better than cure. Following are some alternative methods you can manage RA pain and inflammation with minimal use of medicines:
- Use of dietary supplements is one promising way to manage RA. Studies have shown that use of Omega-3 fatty acid provides effect cure to the symptoms of RA. So, first thing you can do is eat diet full in Omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acid is rich in meat and dairy products.
- Several herbs have also shown promising results in the cure of RA. These herbs include curcumin, Devil’s claw, Thunder god vine, and boswellic acid.
- Acupuncture therapies have also shown to lessen the pain and inflammation seen in patients with RA.
- To minimize the pain associated with RA, you can try massaging the affected area with olive oil.
- Taking hot baths or try applying hot or cold presses on the affected joints. It is very beneficial in limiting the pain and inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
| Written by: | Michal Vilímovský (EN) |
|---|---|
| Education: | Physician |
| Published: | January 30, 2014 at 10:55 AM |
| Next scheduled update: | January 30, 2016 at 10:55 AM |
Related articles
Get more articles like this in your inbox
Sign up for our daily mail and get the best evidence based health, nutrition and beauty articles on the web.



Ache in left arm that you should not ignore
Alkaline water dangers: why you should not drink it
How to Avoid Sleepiness While Studying?
23 Foods That Increase Leptin Sensitivity
Low dopamine (e.g. dopamine deficiency): causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options
Swollen taste buds: the ultimate guide to causes, symptoms and treatment
Thin endometrial lining: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Pimples inside nose: the complete guide
Holes in tonsils: definition, symptoms, treatment and prevention
How to deal with an ingrown hair cyst
Allegra vs. Zyrtec vs. Claritin
Allergy to penicillin and alternative antibiotics
How to get rid of phlegm (excessive mucus) in throat? Detailed guide to medical and home remedies, symptoms and causes
What causes stomach ache after meals?
Liver blood test results explained