Yeast infection: causes, symptoms, complications and treatment options
In this post we shall have a detailed look at causes, symptoms, complications and various natural and drug treatment options for yeast infections.
What is yeast infection?
Yeast infection or cadidiasis is the fungal infection caused by fungi of genus Candida. The fungus that most commonly cause infection is named as Candida Albicans. Candia Albicans lives in our body even in normal and healthy conditions. Candida normally lives in skin and mucous membranes of mouth, gastrointestinal tracts and vagina in females. But the presence of this fungus in our body does not pose any threat to our health. There is no chance to get infected by Candida in normal circumstances because its growth is kept regulated and checked. However, the conditions that promote the overgrowth and rapid multiplication of this yeast like fungus are likely to cause the development of signs and symptoms of yeast infection. The areas that are most commonly targeted by yeast infection include mouth, skin, urinary tract, stomach and genitals.
Types of yeast infection
According to the location or area involved in infection, the yeast infections are of following types:
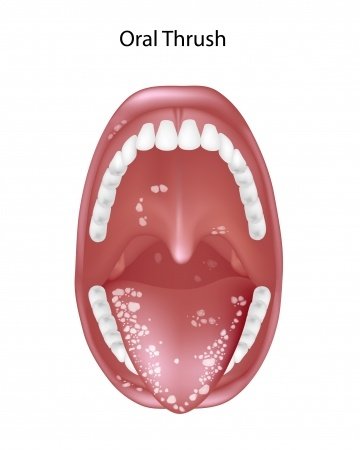
- Oral yeast infection: Mouth cavity contains Candida fungus and a number of bacteria but their healthy balance does not cause infection. The overgrowth of Candida fungus in mouth cavity causes yeast infection. The yeast infection of mouth is also known as “oral thrush” or “oral Candidiasis”.
- Cutaneous yeast infection: Cutanoeus yeast infection is the fungal infection of skin. The yeast infection of skin is very common and it affects the areas that are moist and warm like skin of armpits, groin area, under the breasts, around the edges of nails and corners of mouth. Skin yeast infections are seen very often in the diaper areas of babies that wear diapers. They are also called as diaper rashes.
- Genital yeast infections: Genital yeast infection occurs more often in females. Candida is the natural inhabitant of woman’s vagina. Its overgrowth causes the infection and inflammation of vagina. Almost 75% females get affected by yeast infection once in their lifetime.
Though the women are the common victims of yeast infection, men are prone to it too. Yeast infection can affect the genital areas of men but the chances of yeast infection in men are less than females. There might be a chance that men can get yeast infection from their infected sexual partner but this is very uncommon and rare. However if both the partners are affected, immediate treatment should be given to prevent chances of further spread of infection.
- Invasive candidiasis: In extreme and rare cases, the fungus enters into the bloodstream. Through blood it spreads to various parts of body and causes infection of vital organs like heart, brain, joints, kidney and spleen. This widespread fungal infection is called as candidemia.
Signs and symptoms of yeast infection
Symptoms of skin yeast infection
- Reddish rashes on skin
- White patches on affected areas
- Pustules and blister with redness
- Scaling
- Maceration or softening of skin between fingers and toes.
Symptoms of oral thrush
- Creamy, whitish plaques or patches on tongue, inner side of cheeks, gums and throat.
- Cottage cheese like lesions.
- Pain
- Cracking painful corners of mouth.
Symptoms of genital yeast infection
Vaginal yeast infection shows following features:
- Vaginal irritation and itching
- Burning sensation
- Pain during sexual intercourse and urination
- Inflammation, swelling and redness of vulva
- Soreness
- Thick, whitish, cotton cheese like discharge.
Yeast infection in men shows following symptoms:
- Redness and itching of tip of penis
- Burning pain
- Discomfort during urination
Symptoms of Candidemia
- Flu like symptoms
- Throbbing headaches
- Nasal congestion
- Irritable mood
- Depression
- Fever
- Chronic fatigue
How is the yeast infection caused?
Candida Albicans normally resides in skin and mucous membranes of our body without causing any complication or infection. But what keeps its growth under balance? Why doesn’t it cause infection under normal conditions? A lot of questions might be troubling you right now but all your queries will be answered here. No doubt that this fungus is naturally found within our body but its growth is kept within limited by the immune system of our body. When the number of fungi increases more than limits, the immune systems get activated to wipe off the infection.
Another mechanism by which the growth of candida albicans remains limited is due the presence of some “healthy or friendly bacteria” in body. The vagina and gastrointestinal tract contains some friendly bacteria called “lactobacillus acidophilus” that produces lactic acid. This lactic acid reduces the pH and makes the environment acidic. Fungi cannot survive in this acidic environment and is killed as a result. The healthy balance of friendly bacteria and fungi minimizes the risks of infection and fungal growth. The disturbance in this natural balance may lead to yeast infection because the fungal growth won’t be inhibited anymore.
What factors can cause yeast infection?
- Antibiotics: Use of antibiotics is one of the major reasons behind occurrence of yeast infection. Some antibiotics cannot differentiate between healthy and bad bacteria. So, they not only kill the harmful bacteria but also the healthy bacteria as well. When the friendly lactobacillus bacteria are killed, the natural balance gets upset that allows the fungi to flourish more and more without any restriction.
- Immunosuppression: Immunosuppression means the inability of immune system to work properly. Yeast infections are a common complication in people with immune suppressing diseases like AIDS and cancer. The purpose of immune system is to provide immunity against infection by fighting against the harmful microorganisms. A healthy immune system keeps the growth of Candida Albicans under check but a compromised immune system is unable to control the multiplication of fungus, allowing the fungus to grow in an uncontrolled manner.
- Consuming too much sugar: Consuming too much sugar in diet may increase your chances to get yeast infection especially the oral thrush. Fungus love to eat sugars. It ferments the sugar to get its energy. Eating sugars mean allowing the fungus to grow more and more.
- Diabetes: Diabetic patients are more prone to have yeast infections. In diabetic patients the blood glucose remains always high because the insulin secretion is not enough to metabolize the glucose. The higher the glucose spike, the higher will be the probability for yeast to grow.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women are more likely to develop vaginal yeast infection. In pregnancy the hormonal level gets disturbed. The high estrogen level promotes the storage of glycogen stores in vaginal tissues that makes it a perfect environment for Candida to grow.
- Change in hormones: Taking birth control pills disturbs the hormonal level that promotes the fungal growth and yeast infection. Same thing happens before menses when the hormonal levels get disturbed. Many women feel the symptoms of vaginal yeast infection before menses.
- Stress: Stress may be one of the reasons for yeast infection. In stressful conditions the body tries to adapt by increasing the production of stress hormone called “cortisol”. This steroid hormone suppresses the immune system and increases the blood glucose level, providing a suitable atmosphere for yeast to grow.
- Use of steroids: Having steroid therapy or use of steroid hormone pills increases the risk of yeast infection by suppressing the ability of immune system to fight against flourishing fungus.
- Wearing tight undergarments: Wearing tight undergarments or panties make them moist, damp and warm which provides an opportunity for yeast infection to occur because fungus likes to survive in moist areas of body. Vaginal yeast infection is common in women who wear tight panties for long time.
Complications due to yeast infection
Some complications occurring due to yeast infection are:
- Dysphagia: Dysphagia or difficulty in swallowing is one of the complications associated with severe oral thrush. Persistent infection of oral cavity makes it painful to eat anything.
- Esophagitis: Oral Candidiasis spreads to esophagus and causes its inflammation, leading to a very painful condition.
- Leaky gut syndrome: If the yeast infection persists for a long time, the intestines get too inflamed and become unable to absorb the nutrients. The patient may feel weak and fatigued all the time.
- Spread to other organs: In rare cases, the yeast infection does not remain confined to one part of body. The Candida cells enter into blood and reach the various other organs, leading to many other serious complications like endocarditis, meningitis, arthritis. The organs commonly affected by Candida are lungs, liver, heart, brain, joints and intestine.
- Urinary tract candidiasis: Candida infection can disseminate to urinary tract. Renal Candidiasis is a rare complication of yeast infection that occurs due to spread through blood from site of infection to renal cells. Symptoms of renal candidiasis include abdominal pain, lumbar pain and fever.
- Recurrent infection: If the infection is not treated properly once, there may be a chance that infection comes back again. Recurrent vaginal yeast infection can be very troublesome. Too much scratching of vaginal area causes painful rashes, cracking of skin and sometimes bleeding.
Treatment of yeast infection
Drug therapy
Treatment of yeast infection depends upon the area of the body involved in infection.
- For cutaneous infection: For treating the skin yeast infection medicines like clomitrazole, nystatin, econazole, ketoconazole, ciclopirox are prescribed. In case of infection of nails, drainage of abscesses along with some medicines like fluconazole or itraconazole is recommended.
- For oral thrush: Oral Candidiasis can be treated with medicated lozenges, topical antifungal agents (nystatin and clomitrazole) or oral medicines like fluconazole (diflucan tablets) and itraconazole (sporanox liquid suspension).
In those immunocompromised patient or AIDS patients in which yeast infection is difficult to treat with other anti fungal medication, amphotericin B is the drug of choice.
- For esophageal candidiasis: For esophageal candidiasis, oral or intravenous fluconazole can be given for 2-3 weeks. Alternative drugs for this are itraconazole (sporonax) or ketoconazole (nizoral).
- For vaginal yeast infection: Vaginal yeast infection is usually treated with antifungal creams, ointments, oral tablets and suppositories. The drugs of choice for vaginal yeast infection are miconazole (monistat), teraconzole (terazol), butaconazole (gynazole), clomitrazole, fluconazole (diflucan)
- For systemic infections: Drugs available for systemic candidiasis are fluconazole, voriconazole, caspofungin and amphotericin B.
Natural treatment
Yeast infection is a common matter now that can be treated well at home without eating a handful of medicines. But if the symptoms persist and does not go away with natural remedies, you must consult a doctor for proper treatment.
- Probiotic supplements: Take probiotic supplements of acidophilus, these supplements will replenish the friendly bacteria and will help in restricting the Candida infection.
- Salt water rinses: Rinse your mouth with salt water to reduce the oral yeast infection.
- Look at your diet: Cut down your carbohydrate intake. Take more vegetables and fruit like grapefruits, berries and apples in your diet. Also add virgin olive oil, cod liver oil, fish oil and caprylic acid because they are a rich source of omega fatty acids which boost up the immune system.
- Be careful with antibiotics and steroids: If you suspect that the antibiotic you are taking is the cause of your infection, must consult your doctor then. Other than this, never use steroids on your own without taking doctor’s advice.
- Eat yogurt: Eat yogurt because it is the natural source of lactobacillus acidophilus. Eating yogurt will help in suppressing yeast infection by restoring the balance between healthy bacteria and harmful microorganism.
- Go for the herbs: No doubts the herbal treatment holds its importance for many centuries. These wonderful herbs contain some natural antifungal ingredients that have the tendency to fight the yeast infection. Some herbs with magical anti fungal properties are:
- Garlic: Garlic is the most potent antifungal herb among all other herbs. Chewing fresh garlic cloves or taking garlic capsules helps in curing yeast infection. Garlic cloves can also be used as a remedy for vaginal yeast infections.
- Echinacea: This herb is a powerful booster of immune system. Drinking 2-3 cups of Echinacea tea daily helps in preventing yeast infection.
- Oil of oregano: This oil dehydrates the Candida cells and kills them. Add 2-3 drops of oil of oregano in a glass of water and drink it daily to get rid of yeast infection.
- Neem oil: Neem oil can be applied directly on the affected areas to wipe off the infection.
- Tea tree oil: Tea tree oil is very powerful antifungal. It can be used as mouthwash by diluting 3-4 drops of it with 6 ounces of water or can be applied directly to infected area after mixing with some coconut oil.
- Vinegar: Vinegar contains acetic acid which lowers the pH and makes it difficult for Candida cell difficult to survive. Mix 1 teaspoon of vinegar, 2 teaspoon of honey in a glass of water and drink it daily to prevent yeast infection.
| Written by: | Michal Vilímovský (EN) |
|---|---|
| Education: | Physician |
| Published: | January 26, 2014 at 12:01 PM |
| Last updated: | August 2, 2015 at 5:25 AM |
| Next scheduled update: | August 2, 2017 at 5:25 AM |
Get more articles like this in your inbox
Sign up for our daily mail and get the best evidence based health, nutrition and beauty articles on the web.

Ache in left arm that you should not ignore
Alkaline water dangers: why you should not drink it
How to Avoid Sleepiness While Studying?
23 Foods That Increase Leptin Sensitivity
Low dopamine (e.g. dopamine deficiency): causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options
Swollen taste buds: the ultimate guide to causes, symptoms and treatment
Thin endometrial lining: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Pimples inside nose: the complete guide
Holes in tonsils: definition, symptoms, treatment and prevention
How to deal with an ingrown hair cyst
Allegra vs. Zyrtec vs. Claritin
Allergy to penicillin and alternative antibiotics
How to get rid of phlegm (excessive mucus) in throat? Detailed guide to medical and home remedies, symptoms and causes
What causes stomach ache after meals?
Liver blood test results explained